Thrombi in the heart and coronary arteries
Blood clots in the vessels: arteries and veins - causes, treatment, localization
All materials on the site are published under the authorship or editorship of professional physicians,
but are not a prescription for treatment. Contact the experts!
It is difficult to overestimate the role of the circulatory system, which is the link that allows all parts of the body to function normally. The liquid state of the blood and its normal flow ensure the proper metabolism in the tissues., and, therefore, support its vital activity and the performance of vital functions. Any change, in particular the formation of a blood clot, seriously affects the functioning of the organ and can cause irreversible and very dangerous consequences.
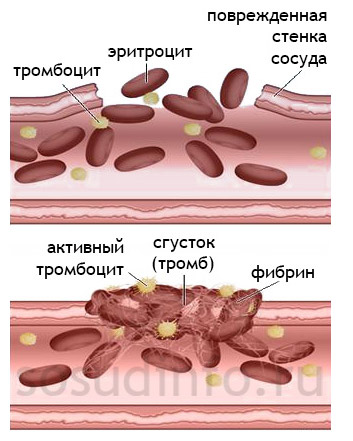
The liquid state of the blood is maintained due to the coordinated work of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems. Under unfavorable circumstances, discoordination of their activities with the occurrence of bleeding or thrombosis is possible.
Clinical signs of thrombosis of a large cerebral artery come down to symptoms: intense headache, loss of sensitivity and motor function in certain parts of the body, impaired speech, vision, memory, etc. If the thrombosis is partial with incomplete occlusion of the lumen of the vessel, then the changes will be chronic with signs of discirculatory,.
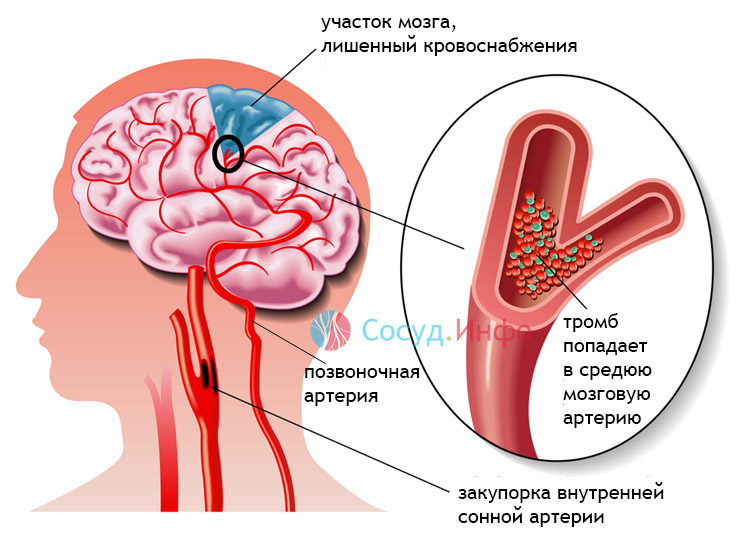
thrombosis of a large cerebral artery - actually a stroke or with the corresponding symptoms and consequences
An embolism of blood vessels in the brain is also possible, when detached blood clots of another localization penetrate into them with blood flow. Signs of such an embolism are also most often caused by necrosis of the nervous tissue (stroke), and among the causes, damage to the valvular cusps of the heart, which occurs with atherosclerosis, syphilis, and septic endocarditis, can be distinguished.
In addition to arterial, a venous thrombus in the head may also occur. Most often, the veins that carry blood from the brain are also affected. The causes of thrombosis are septic conditions with the presence of purulent foci in the skull or outside it. Venous thrombosis is also possible in pregnant women and after childbirth. Among the symptoms of thrombosis of the venous sinuses are severe headache, nausea, vomiting, dysfunction of the cranial nerves, paresis, paresthesia, paralysis, and fever. The described changes threaten the lives of patients and require urgent neurosurgical care and intensive treatment in the intensive care unit.
Thrombi in the heart and coronary arteries
The classic manifestation of thrombosis of the coronary vessels against the background of atherosclerotic lesions is. If the clot does not completely block the lumen of the artery, then chronic coronary artery disease develops in the form of pain in the heart,. In the case of a total closure of the lumen of the vessel, a heart attack will develop: blood will not move through the affected artery and the area of \u200b\u200bthe heart muscle will undergo necrosis (death).
Thrombi in the lungs
As mentioned above, the most common cause of pulmonary thrombosis is embolism from the deep veins of the lower extremities. Blocking the blood flow at the level of the pulmonary trunk inevitably leads to the death of the patient, if the clot is not urgently removed. Most often, patients do not have time to receive timely assistance, since thromboembolism occurs suddenly outside the hospital. Thrombosis of the lobar branches of the pulmonary artery leads to the exclusion of the entire lobe from the breathing process. The mechanism of the pathological effect of massive thrombosis is reduced to a reflex spasm of the coronary arteries, which leads to acute heart failure.
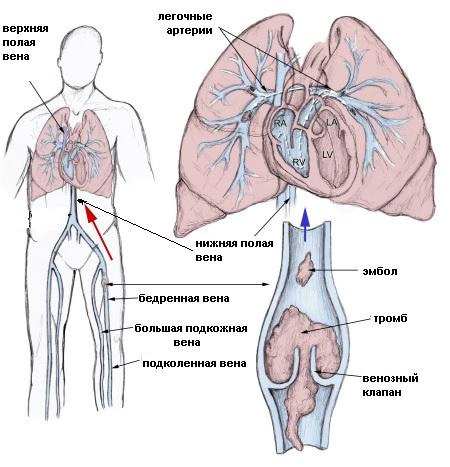
mechanism of PE and areas of risk of thrombosis with subsequent embolism
Symptoms of thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery consist of sudden onset of acute chest pain, severe shortness of breath up to respiratory arrest, cyanosis, and cardiac disorders. Thrombosis of small vessels of the lungs can be chronic relapsing in nature, especially in patients suffering from atrial fibrillation, and their signs will be shortness of breath, dry cough and chest pain.
Blood clots and intestines
Treatment
It is possible to treat thrombosis both in a hospital and at home. Tactics is determined by the localization and volume of vascular lesions.
Thrombus control methods include:
- Conservative medical treatment;
- Operative removal of a thrombus;
- Non-drug methods of influence.
Patients with thrombosis of any localization are shown bed rest, and most often treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Medical therapy implies appointment . One of the most famous and long-used direct anticoagulants is heparin, however, its use is associated with a large number of side effects (allergic reactions, bleeding) and requires careful constant monitoring of hemostasis, therefore, low molecular weight heparins are currently preferred - fraxiparin, clexane, fragmin. These drugs give a significantly smaller number of adverse reactions, are very convenient to use and can be administered independently by the patient himself.
Indirect anticoagulants, such as the anti-clotting drug warfarin, prevent clotting and are usually prescribed for patients with increased risk of thrombosis in patients with an implanted prosthetic valve, chronic heart failure with damage to the leaflets of the valves, and after acute thrombosis, starting from the third day. The use of such drugs should be accompanied by the obligatory control of such an indicator of coagulability as INR, which should not exceed three units.
For prophylactic purposes, patients with cardiovascular disease, with an increased risk of thrombosis due to other reasons, aspirin is often prescribed in a small dose.
(streptokinase, urokinase) designed to dissolve the formed blood clots in the vessels. Their appointment and administration is carried out intravenously by drip and only in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor. Small clots dissolve during thrombolysis, so their introduction is effective in the early stages of the disease, since their later use is fraught with fragmentation of large clots with a risk of pulmonary embolism.
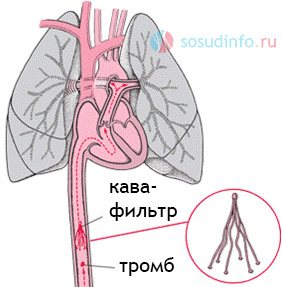
cava filter prevents thrombus embolism in vital vessels
Surgery consists in carrying out or installing a cava filter. In a thrombectomy, the clot is removed by inserting a catheter into the vessel. is a special device that is installed in the inferior vena cava and prevents the penetration and further spread of blood clots into the vessels of the lungs, heart, etc. This operation is especially effective for a floating thrombus, which is fixed to the wall of the vessel at one end, and freely located in the lumen with the other , creating the risk of embolism.
Among non-drug methods to combat thrombosis, elastic bandaging is widespread. Currently, it can be replaced by wearing, which is sold in specialized stores and pharmacies, or is made individually. The degree of compression is determined by a phlebologist, and such underwear should be worn in the morning before getting out of bed.
It should be noted that it is possible to clear the vessels of blood clots only with proper treatment with the use of anticoagulants, thrombolytics, as well as through surgical intervention. Self-medication in case of thrombosis of any localization can be very dangerous.
In case of thrombosis in the vessels of the heart, lungs, brain, in addition to thrombolytic therapy, other measures are taken to maintain and correct the function of these organs.
Prevention: how to avoid thrombosis?
The consequences of thrombosis are often unfavorable and are caused by impaired blood flow in organs and tissues. With arterial thrombosis, the development of a heart attack (heart, brain, intestines, limbs) is possible, with venous thrombosis, especially in the vessels of the legs and small pelvis, there is a high probability of pulmonary embolism. From the side of the thrombus itself, its inflammation is possible with the involvement of the vein wall (), fragmentation, the attachment of a secondary infection.

To avoid thrombosis and its complications, you need to follow simple rules for the prevention of this dangerous condition:
- To give up smoking;
- It is necessary to avoid staying in one position for a long time, taking breaks, raising your legs and warming up with simple exercises;
- Useful walking on stairs;
- In the case of varicose veins, it is necessary to wear compression underwear;
- Foot massage and walking are effective;
- After operations, it is necessary to get up early and activate the patients;
- In the presence of a high risk of thrombosis, effective drug prophylaxis should be carried out.
Thrombosis is a rather dangerous phenomenon, but following the simple rules of work and rest, a healthy lifestyle, and timely preventive measures will help to avoid it.
Video: how to survive when a blood clot breaks off + prevention of thrombosis
Step 2: after payment, ask your question in the form below ↓ At the end of the question don't forget to enter the payment code!
(otherwise you will not be able to identify)
Paid issues are usually processed within 48 hours