What are cookies?
Cookies (translated from English “cookie” literally “pie”, “cookies”) are, one might say, a mark that sites leave on the user’s computer.
When a user repeatedly visits a site, this site, thanks to cookies, already “recognizes” the user (as its own), and often it is not necessary to enter a password.
Therefore, the answer to the question “what are cookies” can be answered that cookies serve to recognize (authenticate) the user when visiting a website again and display “personalized” pages that meet the user’s needs.
Cookies store textual information necessary for the functioning of a particular website, for example, your username and password, while you navigate the site. Then, when moving from one page of a site to a new page of the same site, you will not need to re-enter your password.
Or your e-mail and nickname, which you entered into the form windows when registering on the site, may be stored there. When you open the form, you will no longer need to fill out these fields.
What are cookies in online stores
 Cookies are actively used by online stores. This allows a user who accidentally or deliberately closed the online store or browser window to see his cart with the previously selected items again after the next login to the online store page. This is beneficial for online stores, and convenient for the user, because there is no need to search again for what was selected.
Cookies are actively used by online stores. This allows a user who accidentally or deliberately closed the online store or browser window to see his cart with the previously selected items again after the next login to the online store page. This is beneficial for online stores, and convenient for the user, because there is no need to search again for what was selected.
I like the comparison of cookies to a wardrobe number. The number itself is not particularly valuable, but it allows you to get your coat without any problems.
True, if the number falls into the wrong hands, you may be left without a coat. Likewise, cookies, if they fall into the hands of scammers, can be used against you.
For example, cookies can store the amount that needs to be paid for purchases, for example, in an online store. A fraudster (or hacker) can change this amount in cookies to a smaller amount so that he can put the difference in his pocket.
How do websites recognize users using cookies?
Let's look at a simple example of how user authentication (recognition) occurs using cookies. Let's say you register on the Mail ru website for the first time.
- In this case, you need to enter a username and password, after which this data is sent for processing to the Mail ru server (that is, to powerful computers where all Mail ru information is stored and processed).
- If you entered your data correctly, then the Mail ru server sends back a successful login page, but with attached cookies containing your identifier. In other words, with the help of cookies, the Mail ru site made its mark and remembered you.
- The next time you visit the site, the browser with which you accessed the site will automatically send cookies with your identifier to the Mail ru server. The server checks the identifier (cookies) of such a user against its database.
- If everything matches, then the browser “recognizes” the user, that is, it automatically substitutes the password on the site, or at least provides the password as a hint. In principle, it’s convenient - the user, without entering a login and password, “flies” into the desired site. If the user has made some settings on the site, then thanks to cookies these settings will be automatically restored.
By the way, when using MailRu, cookies must be enabled.
Sometimes during registration the user is asked: “Remember” or “Save” the data he entered. For example, when registering mail on Mail.ru, as can be seen on, you can check the box next to “Remember” or not check it. If you set it, there is a chance that you will go to Mail.ru mail right away, your data will be entered automatically.
Can cookies harm the user?
Despite the fact that cookies make using websites easier, they also raise certain concerns. For example, sometimes a user may receive files by email that they did not request.
Or, for various reasons, cookies begin to work incorrectly and do not recognize the user. Then the user will not be able to access the site. If cookies do not work correctly, this can sometimes lead to malicious actions by a scammer or hacker.
Cookies are written once, and each time you visit a website, the browser sends them back to the server on which the site is located. Not only servers (on which sites are hosted) can create cookies, but also individual scripts responsible for performing this function.
Are cookies viruses?
A cookie is not a program that can perform certain malicious actions. Cookies are a simple set of data written to a file, so it would be incorrect to call them viruses. They are not able to erase information from your computer and cannot send personal data such as photos or videos anywhere.
Cookies can be temporary or permanent. For example, a server (in other words, a website) stores cookies that are tied to a certain date, after which they need to be rewritten. First of all, this is necessary to improve security.
What are browser cookies?
Cookies also have their disadvantages. For example, they are not tied to the computer, but to the browser, so when you change browser you need to re-identify. In addition, cookies are often sent openly, which allows attackers to hack a session and obtain them by scanning the network.
You need to take care of your cookies and not give them to just anyone. Once you register an account on a website, you can immediately delete all cookies. You can restore your rights using a login and password that are known only to you. However, users rarely delete cookies.
There are situations when you are not at your computer, for example, at work or in an Internet cafe, and after you, a stranger can sit down at this computer and use your account (and you forgot to log out of your account). To do this, a stranger just needs to open, for example, your mail and he will immediately have access to the mail and everything connected with this mail. In Yandex mail, this makes it easy to access Yandex.Money, Yandex.Disk, etc.
In such cases, it is better to clear cookies after each session of working on someone else's computer.
What is clearing cookies?
Many browsers have the ability to clear cookies and also set the expiration date for cookies. To do this, you need to find the appropriate tab in your browser settings and check the boxes in the right places.
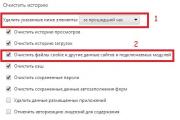
For example, in the Settings of the Google Chrome browser you can find the “Personal Information” tab. It has a “Clear history” button. After clicking this button, a window will open:
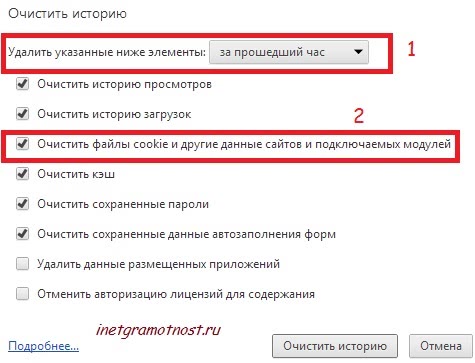 Rice. 2 How to clear cookies in Google Chrome
Rice. 2 How to clear cookies in Google Chrome Here number 2 in Fig. 2 marks the window that is responsible for clearing cookies. Number 1 in Fig. 2, a window is highlighted with which you can set the period for which cookies will be cleared.
For the Mozilla browser, you can see similar tabs for clearing cookies in the article “”. There you can clear the cache and cookies at the same time.
Why clear cookies?
Sometimes this helps when sites are not working correctly.
Many affiliate programs work in such a way that after following an affiliate link from friend X, cookies are recorded in the user’s browser, that is, the cookie records that this user came through the link from friend X. If the user then buys something, then thanks to the cookie, friend X will receive a commission from his affiliate for generating a sale through his link. Therefore, before you click on an affiliate link, sometimes they write that you should first clear your cookies, and then follow my link. This is necessary to ensure that the cookie entry is clean and hassle-free.
P.S. You can also read about internet literacy.